Quick Terrain Modeler Version 8.4.1- Introducing GA3D™!
Applied Imagery is pleased to announce the release of QT Modeler v8.4.1, which enables users to enhance their Geospatial products in a new and exciting way, which we call Geospatial Augmented 3D™ (GA3D™).
For years, users have combined all their geospatial products in QTM (point clouds, DSM/DTMs, imagery, vectors, points), availing themselves of the benefits that the inherent resolution and accuracy of these products delivers. But now users will be able to build on those products and create their own augmented 3D scenes – limited only by your imagination. What does this mean exactly? GA3D™ enables:
- Correction: In cases where you know a DSM is misrepresenting a spatial situation due to inherent limitations of triangulation/surface creation methodologies, (e.g., fences, trees, powerlines), use QTM’s editing tools to smooth or flatten those areas, then use the new QTM OBJ library to insert a 3D object that is more accurate – an actual fence, tree, or powerline. These objects can easily be scaled to the exact dimensions of the actual object. See power lines in the image below.
- Enhancement: Transient objects such as vehicles and aircraft can be added to the scene to enhance situational awareness and represent a situation as-is. See the helicopter in the image below.
- Simulation: In cases where you want to simulate something that may just be in the planning stages (e.g., a new base camp, housing subdivision), GA3D™ enables adding tents, buildings, fences, towers and other structures that represent the new configuration, which, in turn, facilitates a variety of analyses and subsequent decision making.
GA3D™ is enabled by QTM’s support of OBJ 3D mesh files in two distinct implementations: First as a new type of 3D model – just like point clouds and surface models, and second as an attachment to a marker (e.g., an OBJ helicopter model that can be moved around the 3D scene, just like markers). QTM v8.4.1 will include a built-in library of 3D OBJ files (aircraft, vehicles, infrastructure, etc.), but users can create and import their own OBJ models (e.g., in Blender), or import OBJ models from a wide variety of online sources.
In addition to GA3D™, QTM v8.4.1 also adds a 3D model georegistration tool, upgrades to markers, enhancements to flight route planning, a more comprehensive GRG creation tool, route timing analysis enhancements, new movie creation capabilities, and much more. Read on for details!

GA3D™: Precision 3D Data + OBJ Files = The Best of Both Worlds:
QT Modeler v8.4.1 implements OBJ mesh model support two ways:
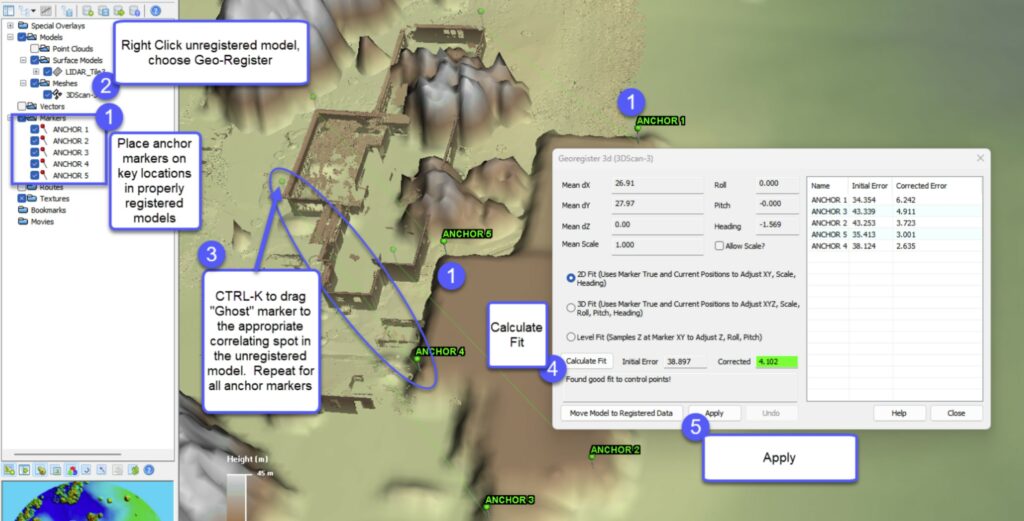
- As a Model: Prior to v8.4.1, QTM supported two types of 3D model: Point Cloud (LAS/LAZ files) and Surface Models (DSM, DEM, DTED, etc.). Now QTM can import 3D mesh models in OBJ format, which opens exciting possibilities of fusion of different types of 3D data – and registering it together.
- As a Marker: The marker implementation of OBJ files enables the placement of 3D objects in the scene, thus expanding QTM’s capabilities into the realm of simulation. For example, users can calculate suitable helicopter landing zones (HLZ), then place a properly scaled 3D model of a helicopter, along with potential obstructions near the HLZ or along the approach (see image above and below). In addition, these 3D models will cast shadows for Line of Sight and substitute for a plain marker pin in the Travel Route Analysis tool and Vector Line of Sight. The increase in realism can be shocking. While QTM will incorporate a library of OBJ files, users can create and import their own, with unlimited possibilities.

Marker Enhancements:
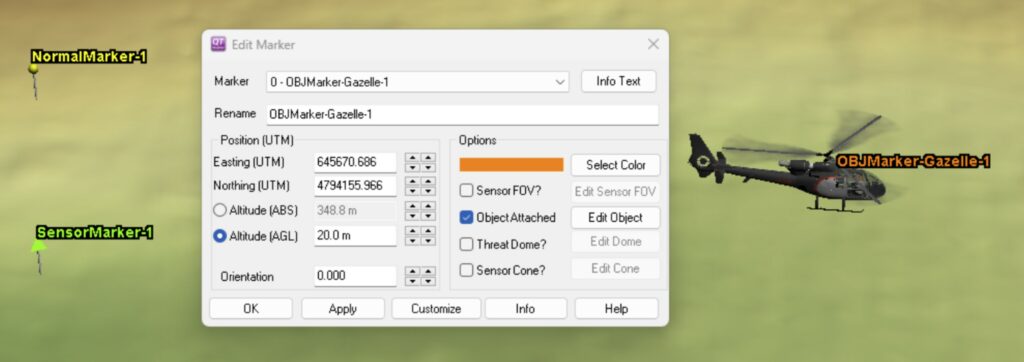
Markers have evolved to be much more than a simple push pin that marks a position. In addition to a 3D location, QTM’s markers have the following optional attachments and attributes, which are visible in the new Edit Marker window:
- Sensor: Use as the basis for Line of Sight Calculations
- Object: 3D OBJ file such as aircraft or vehicles that can be dragged/rotated around the scene as you move the marker. See helicopter in the image below.
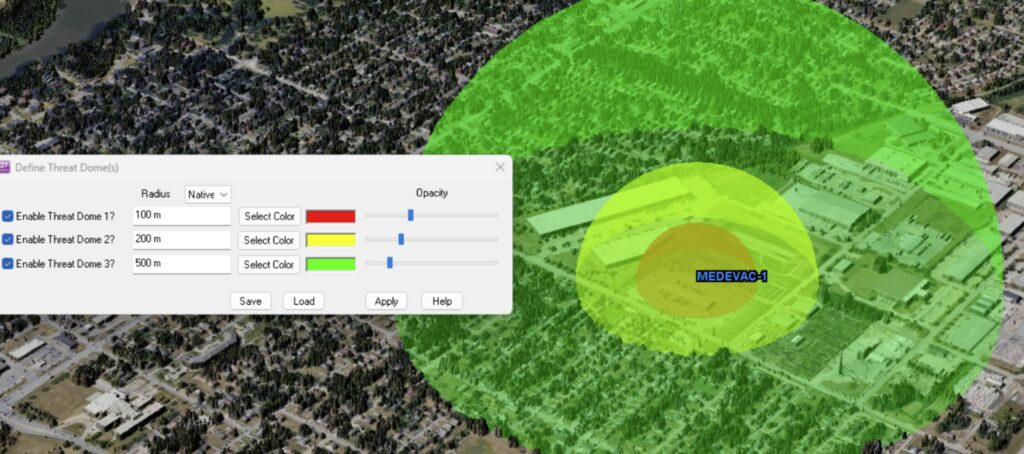
- Threat Dome: Up to three concentric translucent spheres centered on the marker and at specific distances. See image above.
- Sensor Cone: Fully adjustable cone centered on the marker that can be configured and will illustrate sensor coverage from a specific point (the marker).
- Orientation: QTM markers now have a specific orientation and can be rotated by K + Right Click/drag (just like vectors are rotated). Objects, Sensors, and Sensor Cones will rotate with the rotating marker.
3D Georegistration Tool:
Reworked Threat Domes:
Enhanced Movie Creation – Third Person View Tools:
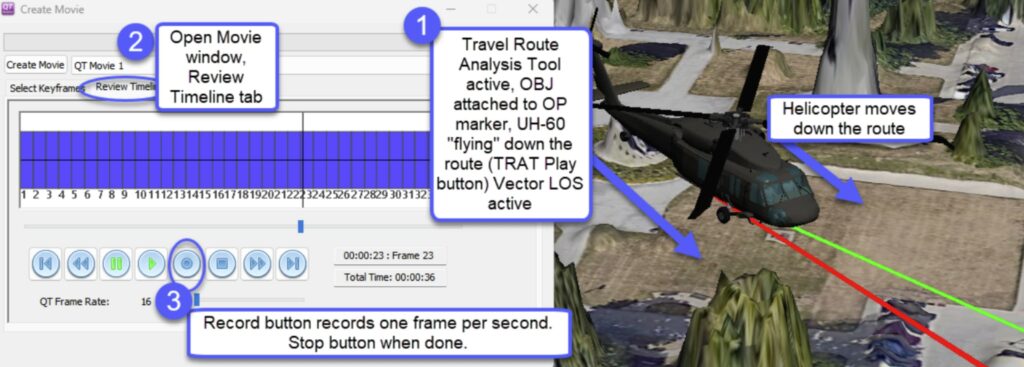
QTM’s movie creation tools have been enhanced to capture many more items in the 3D view – including Vector Line of Sight, Virtual Line of Sight, and 3D OBJ mesh models attached to markers. One of the many benefits is the ability to attach an OBJ aircraft model to the Travel Route Analysis Tool (TRAT), establish a flight route Above Ground Level (AGL), set it in motion in the TRAT playback tool. Then manipulate the 3D scene, capturing a “third person” perspective movie. Then export to MP4 or other movie formats.
Better Flight Route Planning Tools:
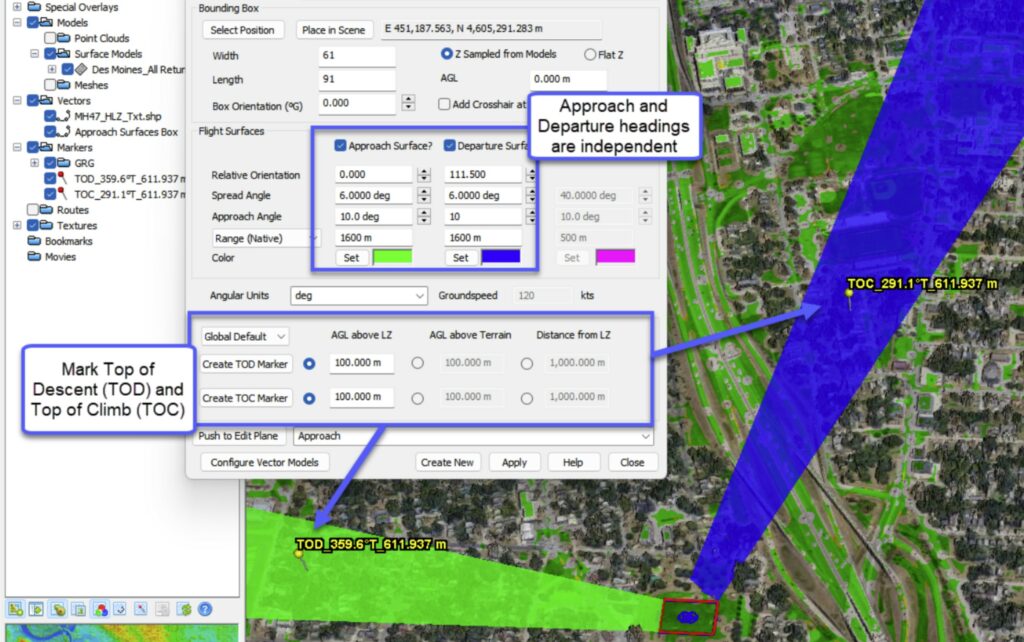
QTM’s Flight Surfaces/Bounding Boxes (FSBB) tool now enables independent heading offsets for the approach and departure surfaces (they used to be fixed 180 degrees apart from each other). This enables very flexible screening for flight obstructions. In addition, users can calculate and mark Top of Descent (TOD) and Top of Climb (TOC) once approach and departure settings are finalized.